The Verb “To Be”
HeyGen Introduction Video
Content
The verb “to be” can be used in the past, the present, and the future. These variations in time are called “tenses”. For now, we will focus on the easiest tense: the present simple.
We can use the present simple of the verb “to be” to talk about situations and states in the present.
- Names:
“I am Maria.”
“He is John.” - Feelings:
“I am excited!”
“She is sad.” - Age:
“I am 12 years old.”
“We are 13 years old.” - Location:
“I am in school.”
“They are at home.” - Nationality:
“I am Ecuadorian.”
“You are American.”
Conjutations
As you can see in the examples above, the verb “to be” changes depending on the subject (who or what we are talking about). This is called “conjugation” – changing a verb to match the subject.
There are three conjugations of the verb “to be”, as shown in red in the next table.
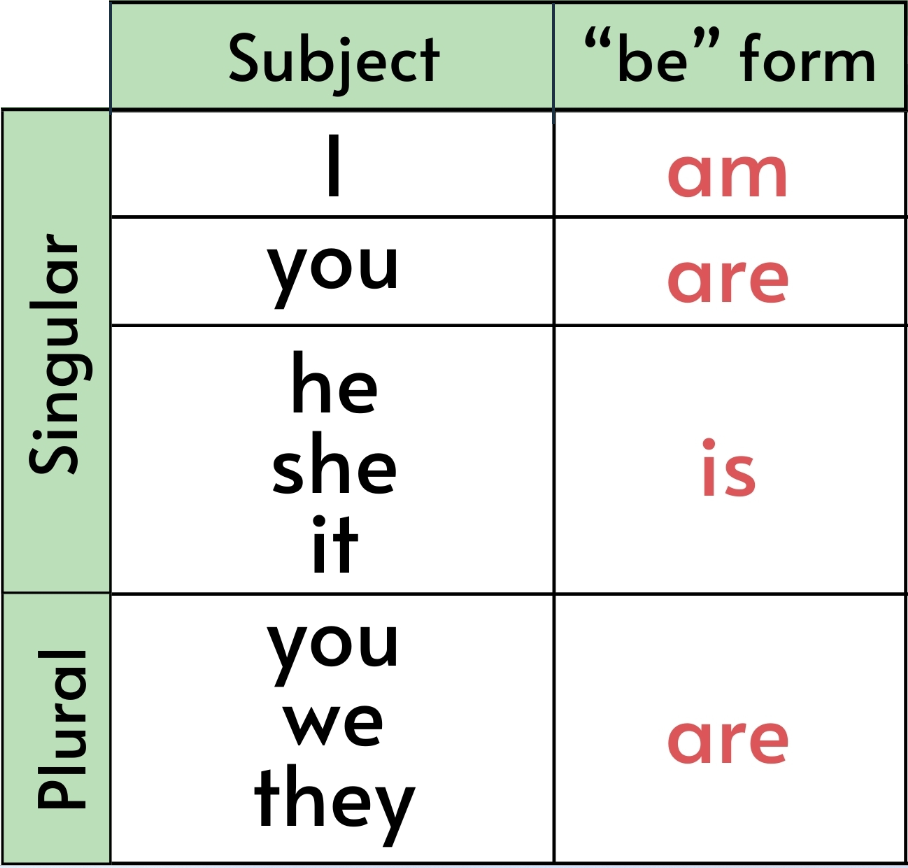
Why are there two “you” in the table? Well, remember that “you” can refer to both a single person o a group of people. But in both cases, we use “are” as the form of the verb ‘to be’ in the present simple.
Questions
To make a question with “to be,” we simply move the correct form of the verb “to be” to the beginning of the sentence. This means the verb comes before the subject. For example:
- I am → Am I?
Example: “Am I late?” - He is → Is he?
Example: “Is he your brother?” - She is → Is she?
Example: “Is she happy?” - You are → Are you?
Example: “Are you okay?” - We are → Are we?
Example: “Are we ready?” - They are → Are they?
Example: “Are they in class?”
Here is a video to help you remember what we’ve seen so far.
Negative form
To make a sentence negative, we add “not” after the verb “to be”.
For example:
- I am → I am not
Example: “I am not tired.” - He is → He is not
Example: “He is not here.” - She is → She is not
Example: “She isn’t happy.” - You are → You are not
Example: You are not ok.” - We are → We are not
Example: “We are not ready.” - They are → They are not
Example: “They are not my friends.”
Contractions
A contraction is a shorter way of saying or writing a word. It’s made by putting two words together and leaving out some letters. These missing letters are replaced with an apostrophe (‘).
In the case of the verb “to be”, we combine the subject and the verb and leave out some letters. The missing letters are replaced by an apostrophe (’). We have both positive and negative contractions.
Positive Contractions with “To Be”
- I am → I’m
Example: I’m happy. - You are → You’re
Example: You’re my friend. - He is → He’s
Example: He’s tall. - She is → She’s
Example: She’s my sister. - It is → It’s
Example: It’s cold today. - We are → We’re
Example: We’re ready to go! - They are → They’re
Example: They’re in the park.
Negative Contractions with “To Be”
We can also shorten “not” in some negative sentences.
- I am not → I’m not
Example: I’m not tired. - You are not → You’re not or You aren’t
Example: You’re not late. or You aren’t late. - He is not → He’s not or He isn’t
Example: He’s not here. or He isn’t here. - She is not → She’s not or She isn’t
Example: She’s not happy. or She isn’t happy. - It is not → It’s not or It isn’t
Example: It’s not raining. or It isn’t raining. - We are not → We’re not or We aren’t
Example: We’re not ready. or We aren’t ready. - They are not → They’re not or They aren’t
Example: They’re not here. or They aren’t here.
The table below summarizes everything we’ve reviewed in this lesson about the different forms of the verb ‘to be’ in the present simple.
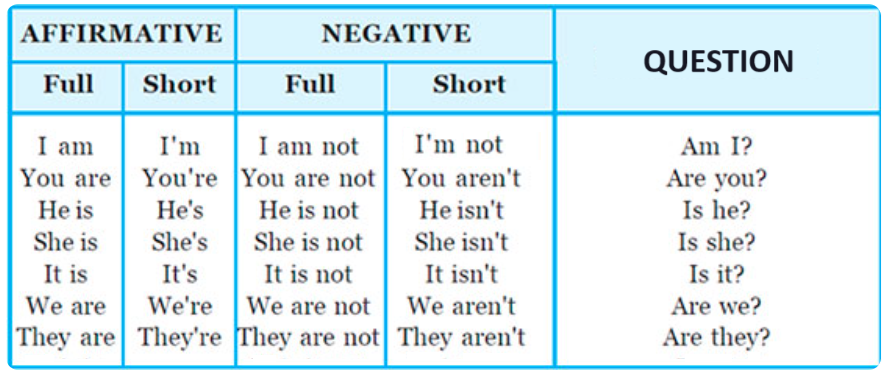
Have fun practicing on the webpage below, and try some of the free games too!
Click here for ‘the verb to be’ games and activities!
Practice Zone
Fill in the gap Activity
Click here to access the “To Be” gap fill activity
