Regular verbs and irregular verbs are two categories of verbs in English, differentiated by how they form their past tense.

Regular Verbs
- Definition: Regular verbs form their past tense and past participle by adding
-edor-dto the base form of the verb. - Examples:
- Walk → Walked (past simple and past participle)
- Play → Played
- Look → Looked
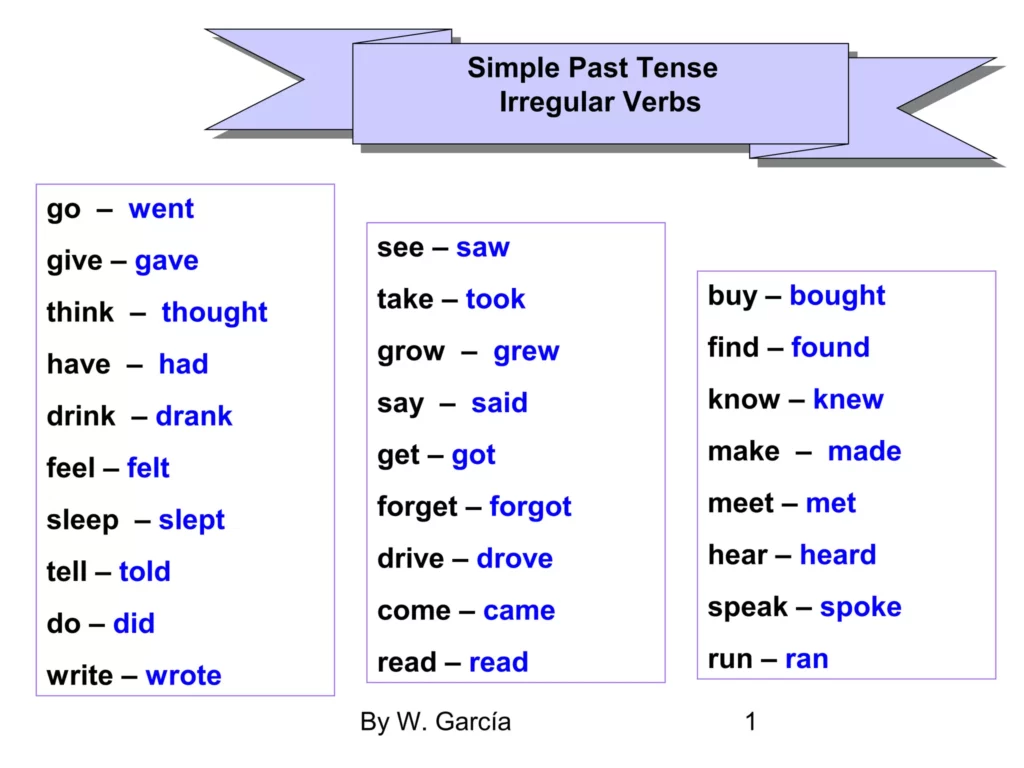
Irregular Verbs
- Definition: Irregular verbs do not follow a consistent pattern when forming their past tense. Each irregular verb has its own unique form.
- Examples:
- Go → Went (past simple)
- See → Saw
- Take → Took
Key Differences:
- Regular verbs follow a predictable pattern (
-edor-d). - Irregular verbs must be memorized because they do not follow a regular pattern and can change in unexpected ways.
Understanding these two categories is crucial for using the correct verb forms in different tenses.
Learning Activities:
Activity #1: Make flash cards! On one side write the base form of the verb and on the other side write the past simple form. Make one for each of the verbs that you haven’t been able to memorize yet. Keep these flash cards to study and to play different games with peers.
Activity #2: Write “Past Simple Challenge” on the white board. Divide the class in 2 groups. The teacher says a verb in the base form and one student from each group has to participate and they both have to shout the correct past form. The one who says it the fastest wins. Keep score on the white board.
