REPORTED SPEECH

Hey there! In today’s lesson, you’ll be learning how to report what someone else has said—also known as Reported Speech. Imagine you’re telling a friend about a conversation you had earlier, or sharing an important announcement you heard. How do you change the words to report someone else’s speech accurately?
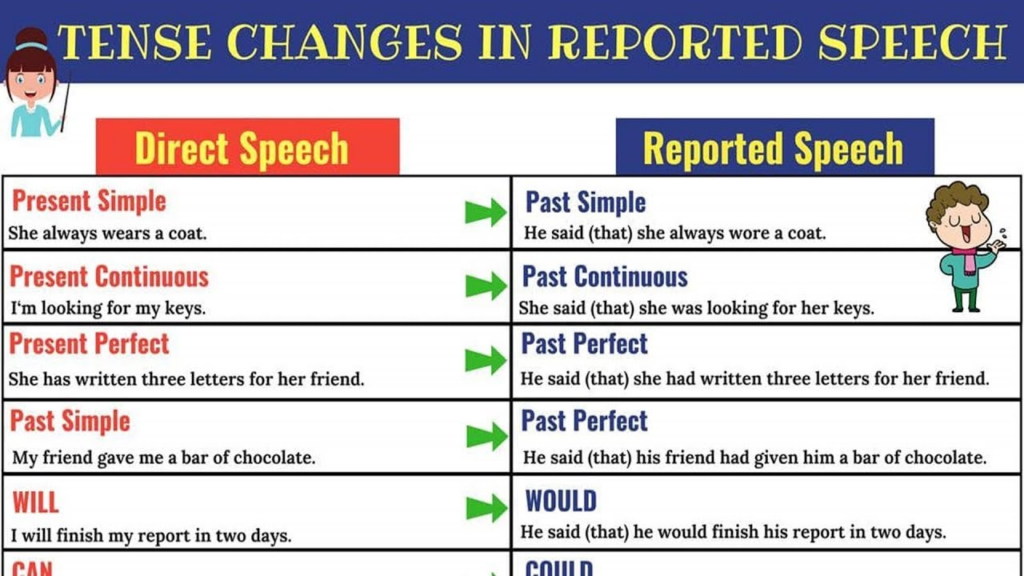
What is Reported Speech?
Reported Speech is when you report or repeat what someone else has said, but you change the structure of the sentence. You do this when telling a story, sharing information, or even gossiping!
For example:
- Direct Speech: He said, “I am going to the store.”
- Reported Speech: He said that he was going to the store.
Notice the changes:
- Tense: Present → Past (“am going” becomes “was going”)
- Pronouns: “I” becomes “he”
- Added “that”: Often we add “that” to connect the sentences
Different Uses of Reported Speech
Reported speech involves changing direct speech to report what someone said, adjusting tense, pronouns, and time expressions. For statements, questions, and requests, different rules apply, such as changing word order or adding “if” for questions. Additionally, time expressions often shift when reporting speech. Below is more detailed information on how to apply these changes.
Learning Activities
Engage in the following activities to practice what you’ve learned throughout this lesson:
Find the Reported Speech
Instructions:
- The teacher will write 5-10 sentences on the board, each in direct speech. For example: “I am tired,” “Can you help me?”
- Your task is to convert each sentence into reported speech.
- Example:
Direct Speech: “I am going to the park.”
Reported Speech: He said that he was going to the park.
- Example:
- Work in pairs to complete the activity. Once you’re done, we’ll check the answers together as a class.
Interview and Report
Instructions:
- Pair students up. One student will be the interviewer, and the other will be the interviewee.
- The interviewer asks 5-10 questions, and the interviewee answers.
- After the interview, the interviewer will report what the interviewee said.
Example:
Interview Question: “What do you want to be when you grow up?”
Reported Answer: He said that he wanted to be a doctor.
