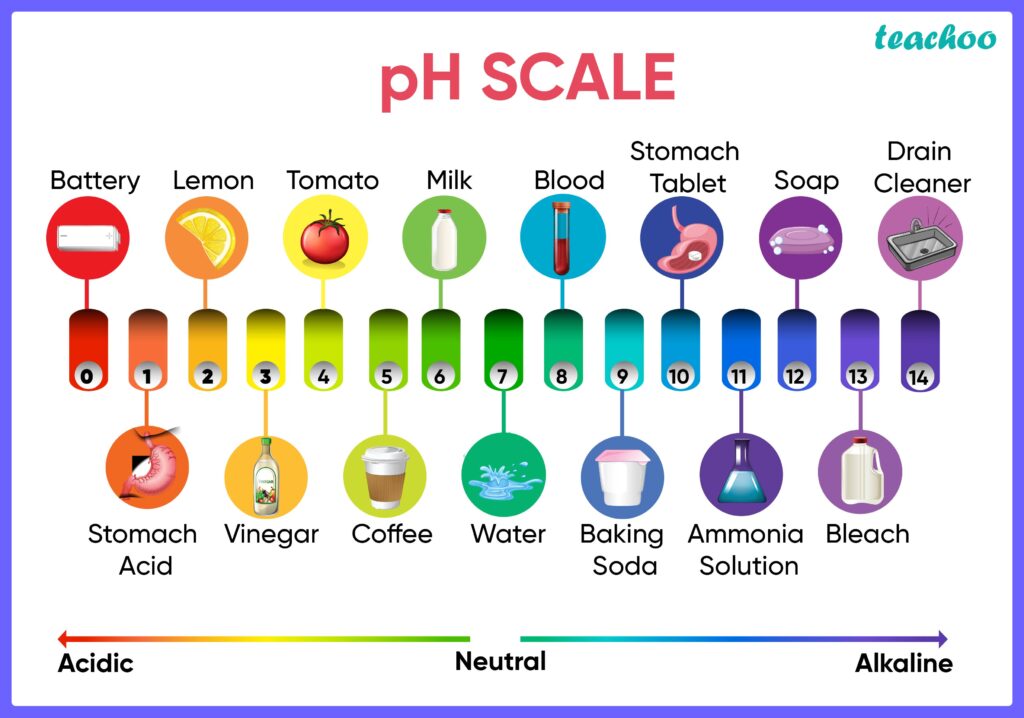
pH of solutions
Learning goals:
Identify compounds as Brønsted-Lowry acids, bases, and conjugate acid-base pairs, using proton-transfer reactions to justify the identification. Given an arbitrary mixture of weak and strong acids and bases, determine which species will react strongly with one another, and what species will be present in large concentrations at equilibrium.
Identify a given solution as containing a mixture of strong acids and/or bases, and calculate the pH and concentrations of all chemical species in the resulting solution.
Resources:
https://classroom.google.com/c/NjA4NDQ0MDQwNzkx/m/NjMzMjgwNTY3Mzcy/details
https://classroom.google.com/c/NjA4NDQ0MDQwNzkx/m/NjE1OTA3MjkyNTk3/details
https://classroom.google.com/c/NjA4NDQ0MDQwNzkx/m/NTU0NDg3MDY4MzMy/details
Learning activities:
Learning by doing. Los estudiantes identificarán de forma cualttativa el pH de distintas soluciones, utilizando tiras de pH, e indicadores industriales y de fuente natural. Problem solved learning: Estudiantes realizarán ejercicios sobre el tema.
Learning by doing: Los estudiantes calcularán la concentración de Hidrógenos positivos e iones oxidrilos de distintas muestras, basados en el pH reportado en las tiras de pH y si es posible, se compará con el valor de un potenciómetro.
