PRESENT SIMPLE

Objectives
- Understand how to use the present simple tense correctly.
- Recognize the importance of the present simple in daily communication.
Content
BASIC STRUCTURE
The basic structure is: Subject + base verb
Example: “I (subject) jump (base verb) high“
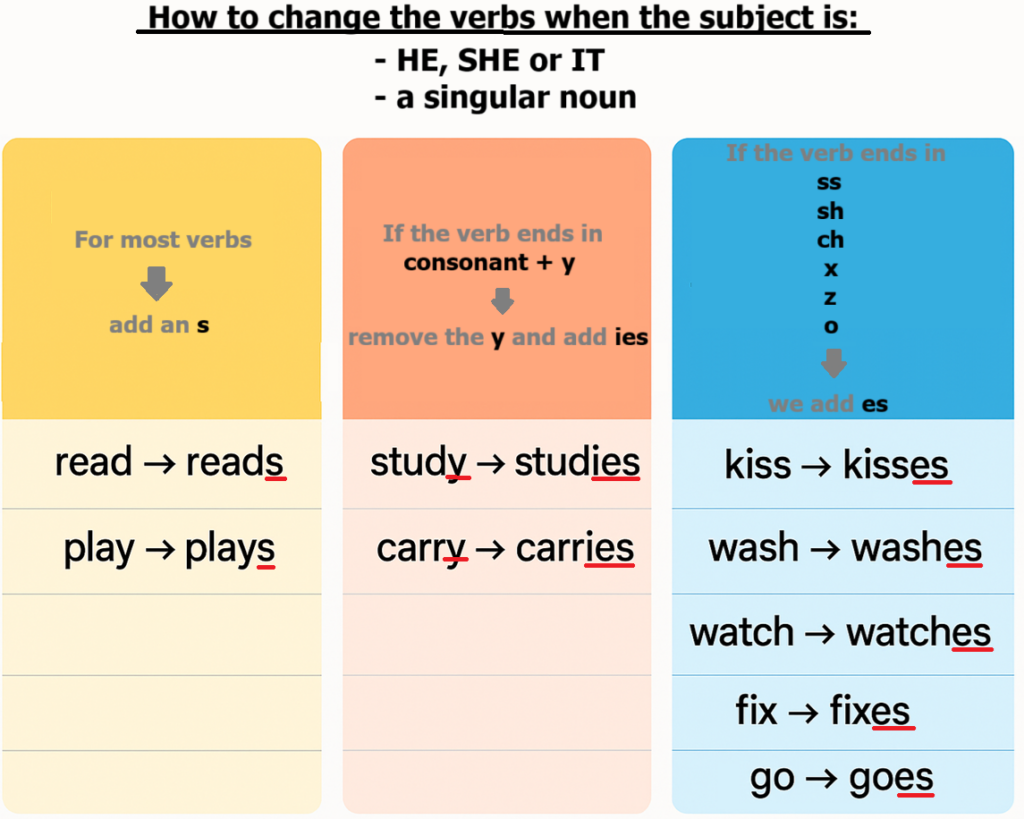
Be aware that you need to add “s”, “es“, or “ies” to the base form of the verb when the subject is in the third person singular (he, she, it).
We also need to make these changes when the subject is a singular noun, such as “mum”, “school”, or “door”.
Examples:
“I eat pasta.” -> “She eats pasta.”
“I finish school at 2:40 pm.” -> “He finishes school at 2:40 pm.”
“I study a lot.” -> “She studies a lot.”
“I cook well.” -> “My mum cooks well.”
The rules for how to change the verbs when the subject is he, she, or it are summarized in the next image. Again, these rules also apply if the subject is a singular noun.
Of course, there are exceptions to these rules. These exceptions are known as “irregular verbs”. Here are some of them and their present simple forms when using the third person (he, she, it) or a singular noun:
be -> is
have -> has
choose -> chooses
can -> can
FORMS
Keep in mind that there are also specific forms of this tense, which will be explained next:
- Affirmative Form:
- Structure: Subject + base form of the verb
- Examples:
He plays football.
She works at the bank.
- Negative Form:
- Structure: Subject + do/does not + base verb
- Examples:
He does not play football.
I do not like spinach
- Interrogative Form:
- Structure: Do/Does + subject + base verb?
- Examples:
Does she work here?
Do you play the guitar?
Practical Examples:
- “I watch TV on Sundays.”(affirmative)
- “I don’t watch TV on weekdays.” (negative)
- “Does he watch TV often?” (interrogative)
USES
- Present Simple for Habits and Routines:
- I walk to school every day.
- She drinks coffee every morning.
- Present Simple for Facts and General Truths:
- Water boils at 100°C.
- The sun rises in the east.
- Present Simple for Scheduled Events:
- The train leaves at 9 AM.
- The movie starts at 7 PM.
Practical Examples:
- “I study English every evening.” (habit)
- “Dogs bark.” (general truth)
- “The bus arrives at 8:30 AM.” (scheduled event)
Here is a video that summarizes the main aspects of this particular verb tense:
Learning Activities
- Routine Tracker Game: Students create a daily routine tracker where they list their activities using the present simple. They earn points by completing tasks that match their routines.
2. Fact or Fiction Quiz: Students are given statements in the present simple and must decide if they are true or false. This activity reinforces the use of the present simple for facts.
3. Schedule Matching: Students receive different schedules (e.g., a school timetable, a movie schedule, etc.) and must match sentences using the present simple to the correct event.
